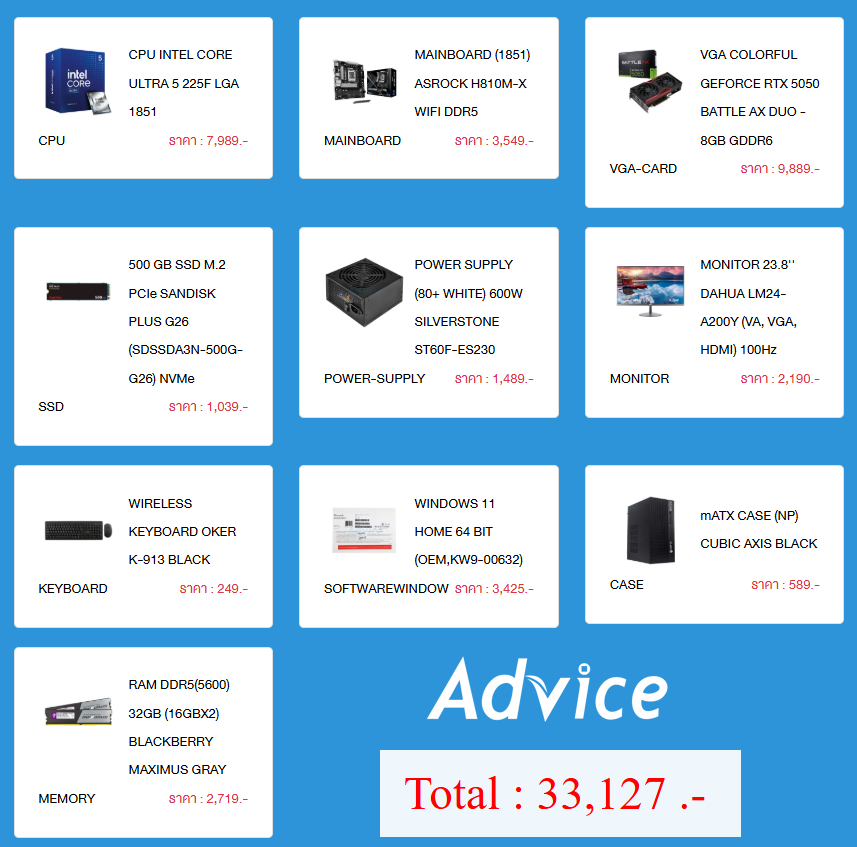
Graduation Quotes To Lead You Into The Next Chapter
Every spring, graduates of colleges and universities around the US are awarded their degrees at commencement ceremonies. “Pomp and Circumstance” will be played, mortarboard caps will be thrown, and a commencement address will be given by a notable figure. The goal of a commencement address is to give advice that can be taken into the “real world” after graduation. It’s an opportunity to reflect on what values are truly meaningful, the importance of education, and how to make a difference. Graduate or not, we can all stand to learn from the words of writers, politicians, musicians, and others. These 12 quotes from some of the most impactful or notable commencement addresses will inspire you, challenge you, and give you a new sense of purpose.
1. “The really important kind of freedom involves attention, and awareness, and discipline, and effort, and being able truly to care about other people and to sacrifice for them, over and over, in myriad petty little unsexy ways, every day.”
—David Foster Wallace, 2005 Kenyon College commencement
myriad
In one of the most famous commencement addresses of all time, “This is Water,” writer David Foster Wallace encouraged graduates to rethink their ideas about freedom. The word myriad [ mir-ee-uhd ] means “of an indefinitely great number; innumerable.” Myriad comes from the Greek for “ten thousand,” and can be used in English to mean the same, but DFW didn’t have this meaning in mind here.
2. “I don’t know what your future is, but if you are willing to take the harder way, the more complicated one, the one with more failures at first than successes, the one that has ultimately proven to have more meaning, more victory, more glory then you will not regret it.”
—Chadwick Boseman, 2018 Howard University commencement
glory
The actor Chadwick Boseman died tragically at a young age from colon cancer. Knowing this makes his words to graduates at his alma mater, Howard, even more poignant. He shares his ideas about how one can achieve glory, “very great praise, honor, or distinction bestowed by common consent; renown.” While today glory has a very positive connotation, this wasn’t always the case. In its earliest uses, glory was used more in the sense of vainglory, “excessive elation or pride over one’s own achievements.”
3. “As every past generation has had to disenthrall itself from an inheritance of truisms and stereotypes, so in our own time we must move on from the reassuring repetition of stale phrases to a new, difficult, but essential confrontation with reality. For the great enemy of truth is very often not the lie—deliberate, contrived, and dishonest—but the myth—persistent, persuasive, and unrealistic.”
—President John F. Kennedy, 1962 Yale University commencement
disenthrall
President John F. Kennedy spent most of his 1962 commencement speech at Yale talking about his vision of government, but he also took time to give advice to the graduates. He says young people need to disenthrall themselves from old myths and stereotypes. Disenthrall is a verb meaning “to free from bondage; liberate.” Thrall is an old word meaning “a person who is morally or mentally enslaved by some power” or, more simply, “slavery.”
4. “[T]hough it’s crucial to make a living, that shouldn’t be your inspiration or your aspiration. Do it for yourself, your highest self, for your own pride, joy, ego, gratification, expression, love, fulfillment, happiness—whatever you want to call it.”
—Billy Joel, 1993 Berklee College of Music commencement
fulfillment
Activist and musician Billy Joel, addressing graduates of the prestigious music school Berklee College, gave advice on how to direct creative energies to making the world a better place. He encourages them to do work for their own fulfillment, “the state or act of bringing something to realization.” Fulfillment is often used to describe the feeling one has when one accomplishes something of personal significance.
5. “I want you all to stay true to the most real, most sincere, most authentic parts of yourselves. I want you to ask those basic questions: Who do you want to be? What inspires you? How do you want to give back?”
—First Lady Michelle Obama, 2015 Tuskegee University commencement
authentic
On a similar note as Billy Joel, former First Lady Michelle Obama exhorts students to be authentic, which here means “representing one’s true nature or beliefs; true to oneself.” The word authentic comes from the Greek authentikós, meaning “original, primary, at first hand.”
6. “I hope you are never victims, but I hope you have no power over other people. And when you fail, and are defeated, and in pain, and in the dark, then I hope you will remember that darkness is your country, where you live, where no wars are fought and no wars are won, but where the future is.”
—Ursula K. Le Guin, 1983 Mills College commencement
future
Science fiction writer Ursula K. Le Guin was no stranger to imagining new worlds and possibilities. So it makes sense that she talked to graduates about the future, “time that is to be or come hereafter.” While today we use future as a noun and adjective, in the mid-1600s, future was also used as a verb to mean “to put off to a future day,” as in They future their work because they are lazy.
7. “As you approach your future, there will be ample opportunity to becomejadedand cynical, but I urge you to resist cynicism—the world is still a beautiful place and change is possible.”
—Ellen Johnson Sirleaf, 2011 Harvard University commencement
jaded
Ellen Johnson Sirleaf is the former president of Liberia and was the first woman to lead an African nation. She spoke at her alma mater, Harvard, about the importance of advocating for change. She notes that many people become jaded as they age, a word that here means “worn out or wearied, as by overwork or overuse.” This sense of jaded comes from the Middle English jade, “a worn-out, broken-down, worthless, or vicious horse.”
8. “Everything meaningful about this moment, and these four years, will be meaningful inside you, not outside you … As long as you store it inside yourself, it’s not going anywhere—or it’s going everywhere with you.”
—Margaret Edson, 2008 Smith College commencement
meaningful
Educator and playwright Margaret Edson told graduates at Smith College that they will carry what is meaningful about their experience with them throughout their lives. Meaningful means “full of meaning, significance, purpose, or value.” Meaningful is formed from a combination of meaning and the suffix -ful, meaning “full of” or “characterized by.” It’s one of many suffixes from Old English that is still present in our language today.
9. “If you really want to fly, just harness your power to your passion. Honor your calling. Everyone has one.”
—Oprah Winfrey, 2008 Stanford commencement
harness
Television host Oprah Winfrey is known for being an inspiration, and her commencement speech at Stanford University in 2008 was certainly inspirational. She urged students to “harness [their] power to [their] passion.” Harness here is being used figuratively and as a verb to mean “to bring under conditions for effective use; gain control over for a particular end.” Harness comes from the Old Norse *hernest meaning “provisions for an armed force.” The word’s meaning has changed quite a lot since! [checking]
10. “When things are going sweetly and peacefully, please pause a moment, and then say out loud, “If this isn’t nice, what is?””
—Kurt Vonnegut, 1999 Agnes Scott College commencement
sweetly
The writer Kurt Vonnegut wanted graduates to take time to reflect on the goodness in life. He describes this as “when things are going sweetly,” a word commonly associated with sugar but that can also describe anything “pleasing or agreeable; delightful.” Sweet is an interesting word that is closely related to its ancient Proto-Indo-European original. You can learn more about the history of the word at our entry for sweet.
11. “From my point of view, which is that of a storyteller, I see your life as already artful, waiting, just waiting and ready for you to make it art.”
—Toni Morrison, 2004 Wellesley College commencement
artful
Novelist Toni Morrison in her commencement address at Wellesley College told graduates she saw their lives as artful. While this word can mean “slyly crafty or cunning; deceitful; tricky,” it is clear from the context that Morrison meant it in the sense of “done with or characterized by art or skill.” In other words, the graduates have the skills, power, and beauty to create a good life.
12. “If I must give any of you advice it would be Say Yes. Say Yes, And … and create your own destiny.”
—Maya Rudolph, 2015 Tulane University commencement
destiny
Graduation is a time to think about the future and one’s destiny, in the sense of “something that is to happen or has happened to a particular person or thing; lot or fortune.” Destiny is often taken to be something that is “predetermined, usually inevitable or irresistible.” But actor Maya Rudolph takes this word in a different direction, saying graduates should “create [their] own destiny.”
Graduation season is a time to consider our own futures, destinies, passions, and desires. We hope these inspiring words give you something to chew on as you go forth into the “real world.”
Copyright 2025, AAKKHRA, All Rights Reserved.
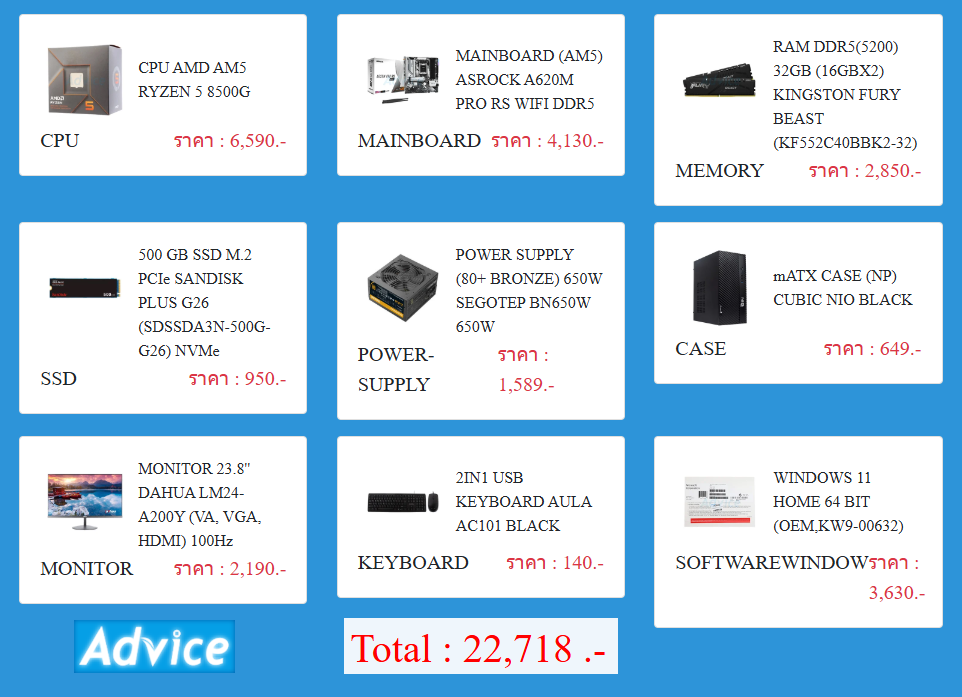
Graduation Quotes To Lead You Into The Next Chapter
Every spring, graduates of colleges and universities around the US are awarded their degrees at commencement ceremonies. “Pomp and Circumstance” will be played, mortarboard caps will be thrown, and a commencement address will be given by a notable figure. The goal of a commencement address is to give advice that can be taken into the “real world” after graduation. It’s an opportunity to reflect on what values are truly meaningful, the importance of education, and how to make a difference. Graduate or not, we can all stand to learn from the words of writers, politicians, musicians, and others. These 12 quotes from some of the most impactful or notable commencement addresses will inspire you, challenge you, and give you a new sense of purpose.
1. “The really important kind of freedom involves attention, and awareness, and discipline, and effort, and being able truly to care about other people and to sacrifice for them, over and over, in myriad petty little unsexy ways, every day.”
—David Foster Wallace, 2005 Kenyon College commencement
myriad
In one of the most famous commencement addresses of all time, “This is Water,” writer David Foster Wallace encouraged graduates to rethink their ideas about freedom. The word myriad [ mir-ee-uhd ] means “of an indefinitely great number; innumerable.” Myriad comes from the Greek for “ten thousand,” and can be used in English to mean the same, but DFW didn’t have this meaning in mind here.
2. “I don’t know what your future is, but if you are willing to take the harder way, the more complicated one, the one with more failures at first than successes, the one that has ultimately proven to have more meaning, more victory, more glory then you will not regret it.”
—Chadwick Boseman, 2018 Howard University commencement
glory
The actor Chadwick Boseman died tragically at a young age from colon cancer. Knowing this makes his words to graduates at his alma mater, Howard, even more poignant. He shares his ideas about how one can achieve glory, “very great praise, honor, or distinction bestowed by common consent; renown.” While today glory has a very positive connotation, this wasn’t always the case. In its earliest uses, glory was used more in the sense of vainglory, “excessive elation or pride over one’s own achievements.”
3. “As every past generation has had to disenthrall itself from an inheritance of truisms and stereotypes, so in our own time we must move on from the reassuring repetition of stale phrases to a new, difficult, but essential confrontation with reality. For the great enemy of truth is very often not the lie—deliberate, contrived, and dishonest—but the myth—persistent, persuasive, and unrealistic.”
—President John F. Kennedy, 1962 Yale University commencement
disenthrall
President John F. Kennedy spent most of his 1962 commencement speech at Yale talking about his vision of government, but he also took time to give advice to the graduates. He says young people need to disenthrall themselves from old myths and stereotypes. Disenthrall is a verb meaning “to free from bondage; liberate.” Thrall is an old word meaning “a person who is morally or mentally enslaved by some power” or, more simply, “slavery.”
4. “[T]hough it’s crucial to make a living, that shouldn’t be your inspiration or your aspiration. Do it for yourself, your highest self, for your own pride, joy, ego, gratification, expression, love, fulfillment, happiness—whatever you want to call it.”
—Billy Joel, 1993 Berklee College of Music commencement
fulfillment
Activist and musician Billy Joel, addressing graduates of the prestigious music school Berklee College, gave advice on how to direct creative energies to making the world a better place. He encourages them to do work for their own fulfillment, “the state or act of bringing something to realization.” Fulfillment is often used to describe the feeling one has when one accomplishes something of personal significance.
5. “I want you all to stay true to the most real, most sincere, most authentic parts of yourselves. I want you to ask those basic questions: Who do you want to be? What inspires you? How do you want to give back?”
—First Lady Michelle Obama, 2015 Tuskegee University commencement
authentic
On a similar note as Billy Joel, former First Lady Michelle Obama exhorts students to be authentic, which here means “representing one’s true nature or beliefs; true to oneself.” The word authentic comes from the Greek authentikós, meaning “original, primary, at first hand.”
6. “I hope you are never victims, but I hope you have no power over other people. And when you fail, and are defeated, and in pain, and in the dark, then I hope you will remember that darkness is your country, where you live, where no wars are fought and no wars are won, but where the future is.”
—Ursula K. Le Guin, 1983 Mills College commencement
future
Science fiction writer Ursula K. Le Guin was no stranger to imagining new worlds and possibilities. So it makes sense that she talked to graduates about the future, “time that is to be or come hereafter.” While today we use future as a noun and adjective, in the mid-1600s, future was also used as a verb to mean “to put off to a future day,” as in They future their work because they are lazy.
7. “As you approach your future, there will be ample opportunity to becomejadedand cynical, but I urge you to resist cynicism—the world is still a beautiful place and change is possible.”
—Ellen Johnson Sirleaf, 2011 Harvard University commencement
jaded
Ellen Johnson Sirleaf is the former president of Liberia and was the first woman to lead an African nation. She spoke at her alma mater, Harvard, about the importance of advocating for change. She notes that many people become jaded as they age, a word that here means “worn out or wearied, as by overwork or overuse.” This sense of jaded comes from the Middle English jade, “a worn-out, broken-down, worthless, or vicious horse.”
8. “Everything meaningful about this moment, and these four years, will be meaningful inside you, not outside you … As long as you store it inside yourself, it’s not going anywhere—or it’s going everywhere with you.”
—Margaret Edson, 2008 Smith College commencement
meaningful
Educator and playwright Margaret Edson told graduates at Smith College that they will carry what is meaningful about their experience with them throughout their lives. Meaningful means “full of meaning, significance, purpose, or value.” Meaningful is formed from a combination of meaning and the suffix -ful, meaning “full of” or “characterized by.” It’s one of many suffixes from Old English that is still present in our language today.
9. “If you really want to fly, just harness your power to your passion. Honor your calling. Everyone has one.”
—Oprah Winfrey, 2008 Stanford commencement
harness
Television host Oprah Winfrey is known for being an inspiration, and her commencement speech at Stanford University in 2008 was certainly inspirational. She urged students to “harness [their] power to [their] passion.” Harness here is being used figuratively and as a verb to mean “to bring under conditions for effective use; gain control over for a particular end.” Harness comes from the Old Norse *hernest meaning “provisions for an armed force.” The word’s meaning has changed quite a lot since! [checking]
10. “When things are going sweetly and peacefully, please pause a moment, and then say out loud, “If this isn’t nice, what is?””
—Kurt Vonnegut, 1999 Agnes Scott College commencement
sweetly
The writer Kurt Vonnegut wanted graduates to take time to reflect on the goodness in life. He describes this as “when things are going sweetly,” a word commonly associated with sugar but that can also describe anything “pleasing or agreeable; delightful.” Sweet is an interesting word that is closely related to its ancient Proto-Indo-European original. You can learn more about the history of the word at our entry for sweet.
11. “From my point of view, which is that of a storyteller, I see your life as already artful, waiting, just waiting and ready for you to make it art.”
—Toni Morrison, 2004 Wellesley College commencement
artful
Novelist Toni Morrison in her commencement address at Wellesley College told graduates she saw their lives as artful. While this word can mean “slyly crafty or cunning; deceitful; tricky,” it is clear from the context that Morrison meant it in the sense of “done with or characterized by art or skill.” In other words, the graduates have the skills, power, and beauty to create a good life.
12. “If I must give any of you advice it would be Say Yes. Say Yes, And … and create your own destiny.”
—Maya Rudolph, 2015 Tulane University commencement
destiny
Graduation is a time to think about the future and one’s destiny, in the sense of “something that is to happen or has happened to a particular person or thing; lot or fortune.” Destiny is often taken to be something that is “predetermined, usually inevitable or irresistible.” But actor Maya Rudolph takes this word in a different direction, saying graduates should “create [their] own destiny.”
Graduation season is a time to consider our own futures, destinies, passions, and desires. We hope these inspiring words give you something to chew on as you go forth into the “real world.”
Copyright 2025, AAKKHRA, All Rights Reserved.